How to operate a drone? This seemingly simple question opens a world of exciting possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to intricate drone racing. Mastering drone operation requires a blend of technical understanding, safety awareness, and practical skill. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of everything you need to know, from understanding your drone’s components to executing advanced maneuvers and capturing stunning visuals.
We w
Understanding drone operation involves mastering several key skills, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. Successfully piloting a drone requires practice and knowledge; a great resource to learn the fundamentals is this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from basic controls to advanced maneuvers. Ultimately, safe and responsible drone operation hinges on thorough preparation and consistent practice.
ill explore the essential pre-flight checks, safe flight procedures, and effective control techniques. Learn how to navigate various flight situations, troubleshoot common problems, and even delve into the art of aerial photography and videography. By the end, you’ll be equipped to confidently take to the skies and unleash the full potential of your drone.
Drone Components and Terminology: How To Operate A Drone
Understanding the individual parts of a drone and the associated terminology is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section will detail the function of each major component and provide a glossary of common terms.
Drone Component Functions

A drone’s functionality relies on the coordinated operation of several key components. Let’s explore each one:
- Propellers: These rotating blades generate thrust, enabling the drone to lift off and maneuver in the air. Different propeller designs offer varying levels of thrust and efficiency.
- Motors: Electric motors power the propellers. Brushless motors are commonly used in drones for their efficiency and longevity.
- Flight Controller: This is the drone’s “brain,” responsible for processing sensor data and controlling the motors to maintain stability and execute flight commands. It integrates data from the gyroscope, accelerometer, barometer, and GPS (if equipped).
- Battery: The power source for the entire system. Lithium Polymer (LiPo) batteries are frequently used due to their high energy density.
- GPS Module (if equipped): Allows the drone to determine its location and maintain a fixed position or follow pre-programmed flight paths.
- Gimbal (if equipped): A stabilized platform that holds the camera, ensuring smooth and steady footage, even during flight maneuvers.
- Radio Transmitter/Controller: The device used to pilot the drone and control its camera. It sends signals to the flight controller, directing the drone’s movements.
- Camera: Captures images and videos. Features vary widely depending on the drone model, including resolution, field of view, and video recording capabilities.
Drone Terminology Glossary
Familiarizing yourself with common drone terms will enhance your understanding and communication regarding drone operation.
| Term | Definition | Term | Definition |
|---|---|---|---|
| Altitude Hold | The drone maintains a constant height above ground level. | Gimbal | A stabilized mounting system for the camera. |
| ESC (Electronic Speed Controller) | Regulates the speed of the motors. | GPS | Global Positioning System; used for location and navigation. |
| LiPo Battery | Lithium Polymer battery, a common power source for drones. | Payload | The weight the drone can carry, such as a camera or other equipment. |
| Return-to-Home (RTH) | A feature that allows the drone to automatically return to its takeoff point. | Throttle | Controls the drone’s vertical movement (up and down). |
| Firmware | The software that controls the drone’s hardware. | Yaw | Rotation of the drone around its vertical axis. |
Drone Diagram
Imagine a diagram showing a quadcopter drone. Each of the four arms extends outwards from a central body. At the end of each arm is a propeller, connected to a motor controlled by the flight controller located in the central body. The battery is housed within the central body, providing power to the motors and flight controller. A camera, often mounted on a gimbal, is typically positioned beneath the central body for optimal image capture.
The GPS module (if present) is also situated within the central body, receiving signals to determine location and aid in navigation. The radio receiver receives signals from the controller, allowing the pilot to control the drone’s movements.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
Before each flight, a thorough pre-flight checklist is essential to ensure safe and responsible operation. This involves checking both the drone and the surrounding environment.
Pre-Flight Checklist
A comprehensive pre-flight checklist should include the following steps:
- Inspect the drone for any physical damage to propellers, motors, or body.
- Ensure the battery is fully charged and properly connected.
- Check the GPS signal strength (if applicable).
- Verify the controller is properly paired with the drone.
- Review the weather conditions – avoid flying in strong winds, rain, or snow.
- Check for any obstacles or obstructions in the flight area.
- Be aware of and comply with local regulations and airspace restrictions.
- Inform others nearby about the drone operation.
Safety Hazards and Mitigation
Several hazards are associated with drone operation, necessitating careful planning and execution.
- Propeller strikes: Keep a safe distance from people and objects during operation.
- Loss of signal: Always fly within visual line of sight (VLOS) and be prepared for signal loss.
- Battery failure: Use high-quality batteries and monitor their charge level during flight.
- Collisions: Avoid flying near obstacles and maintain awareness of the surrounding environment.
- Malfunctions: Regular maintenance and pre-flight checks can help mitigate malfunctions.
Legal Regulations and Airspace Restrictions
Adherence to legal regulations is paramount. These can vary by location and should be thoroughly researched before flying.
- Register your drone with the appropriate authorities (if required).
- Obtain necessary permits or licenses for commercial or specific flight operations.
- Respect airspace restrictions around airports, military bases, and other sensitive areas.
- Maintain a safe distance from people and property during flight.
- Avoid flying near crowds or events without proper authorization.
Taking Off and Landing
Safe and controlled takeoff and landing procedures are fundamental to responsible drone operation. This section will Artikel best practices for both.
Safe Takeoff Procedure

A step-by-step approach ensures a smooth takeoff:
- Power on the controller first, followed by the drone.
- Allow the GPS to acquire a satellite signal (if applicable).
- Calibrate the compass if prompted.
- Slowly increase the throttle to lift the drone vertically.
- Maintain a steady ascent, avoiding sudden movements.
Controlled Landing Techniques
Smooth landings prevent damage to the drone and its surroundings:
- Begin descent slowly, gradually reducing throttle.
- Maintain a controlled rate of descent, avoiding a sudden drop.
- Lower the drone gently to the ground, minimizing impact.
- Power off the drone, followed by the controller.
Takeoff and Landing Techniques Comparison
Different takeoff and landing techniques exist, each with its advantages and disadvantages. For example, a gentle, vertical ascent is suitable for most situations, while a more aggressive, angled takeoff might be used in confined spaces. Similarly, a slow, controlled descent is generally preferred for safety, but a more rapid descent might be necessary in emergency situations. The choice of technique depends on the environment and the pilot’s skill level.
Always prioritize safety.
Controlling Drone Movement
Mastering drone control involves understanding how to maneuver the drone in all directions using the controller. This section details the process of controlling altitude, speed, and direction.
Drone Controller Maneuvers
Most drone controllers use joysticks to control movement. One joystick typically controls altitude and direction (yaw), while the other controls forward/backward and left/right movement.
- Forward/Backward: Move the joystick forward to move the drone forward and backward to move it backward.
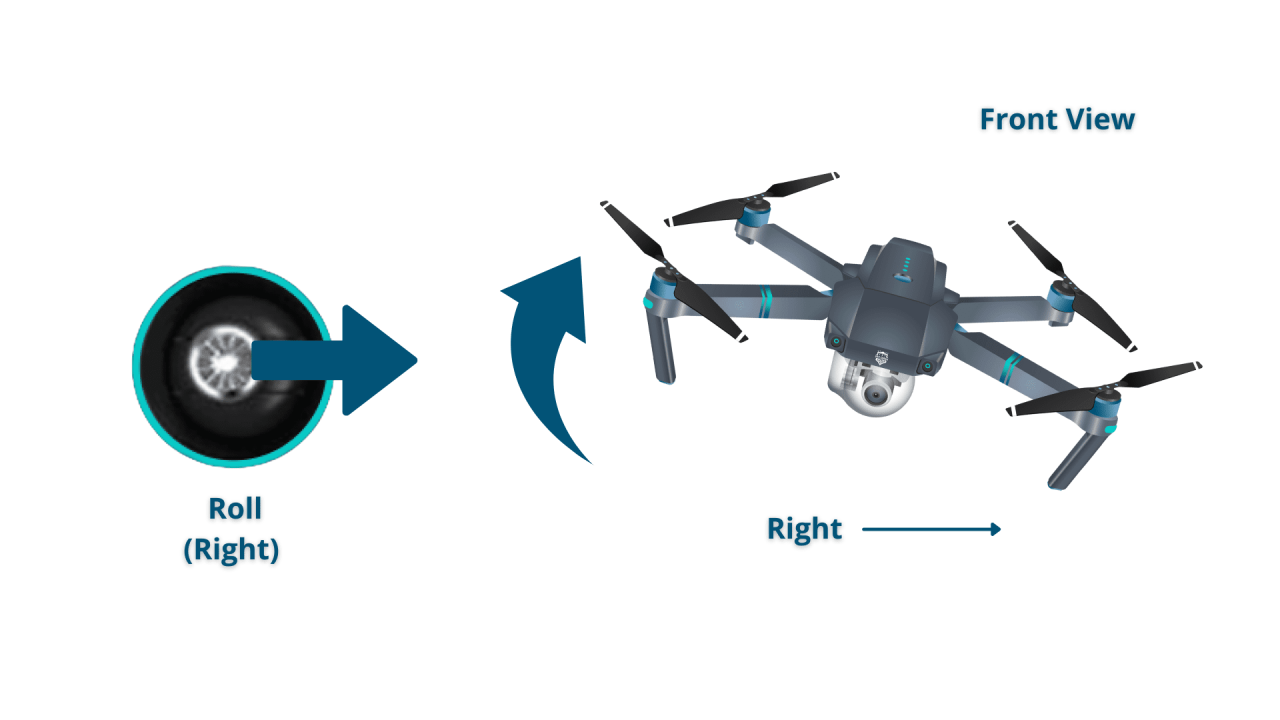
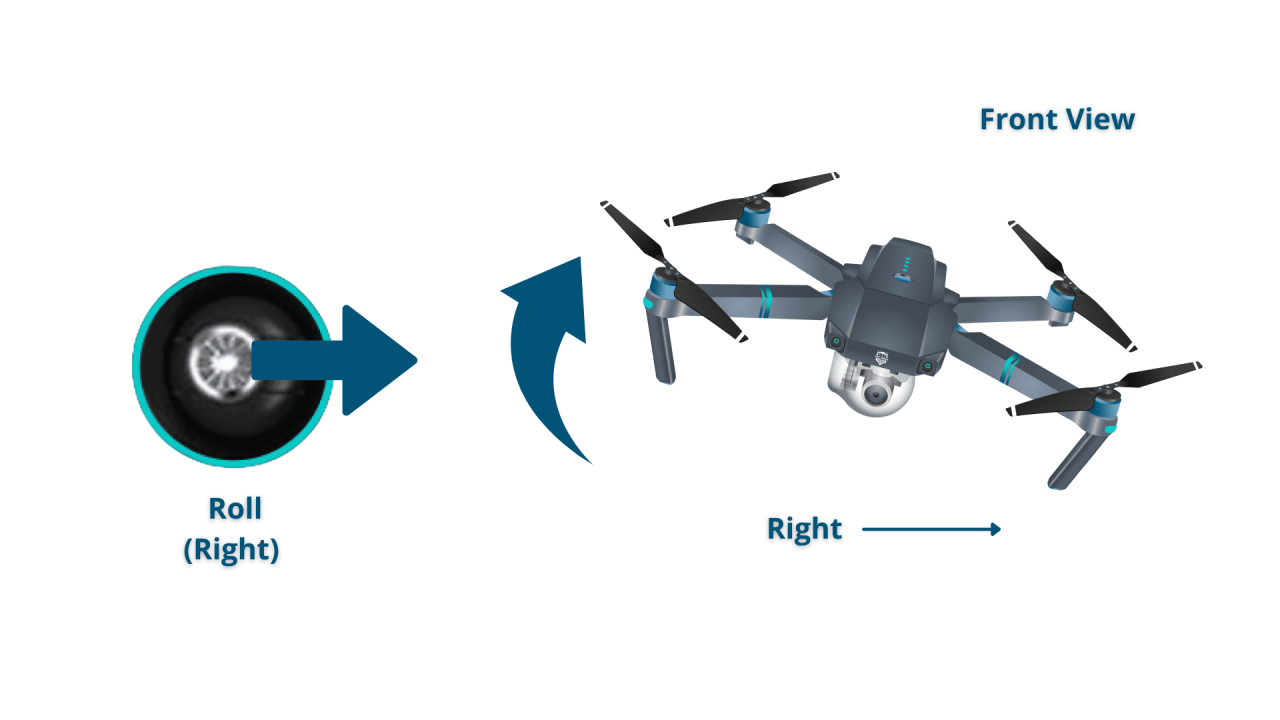
- Left/Right: Move the joystick left to move the drone left and right to move it right.
- Up/Down: Move the joystick upwards to increase altitude and downwards to decrease altitude.
- Yaw (Rotation): Rotate the joystick to rotate the drone left or right.
Adjusting Altitude and Speed
Precise altitude and speed control are essential for smooth and safe flight. Many drones offer adjustable speed settings, allowing pilots to fine-tune the drone’s responsiveness. Altitude control is often achieved through the throttle stick or dedicated altitude hold features.
Obstacle Course Navigation Flowchart, How to operate a drone
Imagine a flowchart illustrating a simple obstacle course navigation. It would begin with the drone taking off and moving forward. Upon encountering an obstacle, the drone would move to the left, then forward again, potentially requiring adjustments in altitude to clear the obstacle. After navigating around the obstacle, the drone would continue forward to the finish line, with potential adjustments to altitude and direction as needed.
The flowchart would visually represent these steps using different shapes (rectangles for actions, diamonds for decisions) and connecting arrows to show the flow of operations.
Drone Camera Operation and Features
Modern drones often include sophisticated camera systems with various modes and settings. Understanding these features is crucial for capturing high-quality images and videos.
Camera Modes and Settings
Typical drone cameras offer a range of modes and settings, including:
- Photo Mode: Allows capturing still images with various settings such as resolution, ISO, and shutter speed.
- Video Mode: Enables recording videos with different resolutions, frame rates, and bitrates.
- Timelapse Mode: Captures a series of images at set intervals to create a timelapse video.
- Panorama Mode: Stitches together multiple images to create a wide panoramic view.
Adjusting Camera Settings for Optimal Image Quality
Proper camera settings are crucial for capturing high-quality images in various lighting conditions. Adjusting settings like ISO, shutter speed, and aperture can significantly impact image quality. In low light, increasing the ISO might be necessary, while in bright light, decreasing the ISO and adjusting shutter speed can prevent overexposure.
Tips for Capturing High-Quality Photos and Videos
Several tips can enhance your drone photography and videography:
- Use the “golden hour” (sunrise and sunset) for optimal lighting.
- Experiment with different angles and perspectives.
- Plan your shots carefully, considering composition and storytelling.
- Maintain smooth and controlled movements during recording.
- Use editing software to enhance your footage.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even with careful preparation, drone malfunctions can occur. This section Artikels common issues, their causes, and troubleshooting steps.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Troubleshooting
| Problem | Possible Cause | Troubleshooting Steps | Additional Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low Battery | Insufficient charge, high power consumption | Charge the battery fully, reduce flight time, check battery health | Consider using a higher capacity battery |
| Loss of Signal | Distance from controller, interference, poor weather | Reduce distance, avoid interference sources, fly in good weather | Always maintain visual line of sight (VLOS) |
| Unexpected Movements | Wind, GPS interference, motor malfunction | Fly in calm conditions, check GPS signal, inspect motors | Calibrate the compass and sensors |
| Drone Fails to Take Off | Low battery, motor issues, software glitch | Charge the battery, inspect motors, restart the drone | Check for firmware updates |
Basic Drone Maintenance
Regular maintenance prolongs the lifespan of your drone and ensures optimal performance. This includes cleaning propellers and the drone body, inspecting motors and connections, and checking the battery health. Always refer to your drone’s manual for specific maintenance instructions.
Advanced Drone Maneuvers
Once comfortable with basic drone control, you can explore more advanced maneuvers. This section covers techniques such as circling, hovering, and precise positioning.
Advanced Maneuver Techniques
Advanced maneuvers require practice and precision. Techniques like circling involve using the yaw control to rotate the drone while maintaining altitude and speed. Precise hovering requires subtle adjustments to the controls to maintain a fixed position in the air. Mastering these techniques enhances your drone piloting skills and opens up possibilities for more creative aerial shots.
GPS and Navigational Aids for Autonomous Flight
GPS and other navigational aids enable autonomous flight features such as waypoint navigation and return-to-home (RTH). These features rely on accurate GPS signals and pre-programmed flight plans. Autonomous flight simplifies complex maneuvers and allows for more creative aerial shots.
Drone Model Capability Comparison
Different drone models vary significantly in terms of maneuverability and flight features. Some drones excel in speed and agility, while others prioritize stability and precision. The choice of drone depends on the intended use and the pilot’s skill level. Consider factors such as flight time, camera quality, and advanced features when choosing a drone model.
Drone Photography and Videography Techniques
Drone photography and videography open up exciting possibilities for creative content creation. This section provides tips for achieving specific effects and creating visually appealing footage.
Achieving Specific Photographic and Videographic Effects
Various techniques can enhance the visual appeal of your drone footage. Cinematic shots can be achieved by using smooth, controlled movements and adjusting camera angles. Aerial panoramas can be created by stitching together multiple images. The use of different camera modes (timelapse, slow motion) can also add visual interest and creative effects. Experimentation is key to discovering new techniques and styles.
Tips for Composing Visually Appealing Drone Footage
Effective composition is crucial for visually appealing drone footage. Use the rule of thirds, lead lines, and other compositional principles to create balanced and engaging shots. Consider the background, lighting, and subject matter when composing your shots. Vary your angles and perspectives to add visual interest and depth to your footage.
Principles of Good Composition and Storytelling in Drone Videography
Good drone videography involves more than just capturing beautiful images. It’s about telling a story through your footage. Plan your shots carefully, considering the narrative arc and the message you want to convey. Use editing techniques to enhance the storytelling aspect of your videos and create a compelling visual experience for your viewers. Consider pacing, music, and sound effects to amplify the emotional impact of your videos.
Operating a drone is a rewarding experience that combines technology, skill, and creativity. From the initial thrill of takeoff to the satisfaction of capturing stunning aerial footage, the journey of learning to fly is filled with opportunities for growth and exploration. Remember that safety and responsible operation are paramount. By following the guidelines Artikeld in this guide, and by continually practicing and refining your skills, you can safely and confidently explore the limitless possibilities of drone flight.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource to get started is this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers. Mastering these skills ensures safe and enjoyable drone operation.
Commonly Asked Questions
What type of drone is best for beginners?
User-friendly drones with GPS stabilization and automatic return-to-home features are ideal for beginners. Look for models with intuitive controls and good flight stability.
How long does a drone battery typically last?
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the model and usage. Expect flight times ranging from 15 to 30 minutes, but always have extra batteries on hand.
What should I do if I lose control of my drone?
If you lose control, immediately attempt to activate the return-to-home function (if available). If that fails, try to bring the drone down safely, and then assess the situation. Contact local authorities if necessary.
Where can I legally fly my drone?
Drone laws vary by location. Check your local regulations and airspace restrictions before flying. Websites and apps providing airspace information are valuable tools.